In today’s competitive landscape, ensuring critical assets’ optimal performance and longevity while minimizing costs and downtime is paramount. However, prioritizing maintenance activities can be challenging, as there are limited resources and numerous assets to manage. Criticality analysis is a powerful tool in asset management and maintenance.
Criticality assessment enables organizations to systematically assess the importance of each asset within their operations, helping them prioritize maintenance efforts based on factors such as asset function, failure consequences, and likelihood of failure.
In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of asset criticality, exploring its significance in ensuring effective asset maintenance strategies and maximizing operational efficiency. Join us as we uncover its fundamental principles and applications and understand its relevance in the broader context of asset maintenance.
Understand Criticality Analysis
Criticality Analysis is a fundamental process utilized in asset management to prioritize maintenance based on the asset’s criticality within the system or facility. It enables organizations to evaluate the importance of each asset function in terms of its impact on safety, operations, production, and overall business objectives.
To access asset criticality, asset function, failure consequences, and the likelihood of failure are required. With the help of those factors, organizations can identify the assets that need the most attention and resources for upkeep and maintenance, enabling them to assign resources more effectively, reduce downtime, and optimize asset performance and reliability.
Fundamental Concept of Criticality Analysis
Asset Criticality is built upon various concepts that form the foundation for evaluating and prioritizing organizational assets. Understanding these concepts is essential for effectively implementing and interpreting critical analysis results.
Asset Prioritization
Critical discourse analysis is an essential process organizations use to prioritize their asset effectively. It considers various factors such as safety, financial impact, failures, and production impact. Businesses can distribute resources more effectively by identifying holdings with the highest impact on operations.
“It ensures that maintenance efforts are directed appropriately.” The proactive asset criticality assessment minimizes downtime, optimizes overall asset performance, and enhances safety. Through Criticality analysis for maintenance purposes, Organizations gain insights into their asset portfolio’s strategic importance, empowering them to gain insights into their asset portfolio’s strategic importance.
Asset prioritization enables organizations to make informed decisions and allocate resources to reduce operational efficiency and mitigate potential risks associated with asset failures.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is vital in identifying and reducing potential risks associated with asset failures. By evaluating factors such as environmental impact, regulatory compliance, and health and safety implications, organizations can proactively develop strategies to minimize risks.
It safeguards against potential hazards but also ensures compliance with regulations and standards. Through comprehensive risk assessment or criticality analysis, organizations can effectively manage risks, enhance operational safety, and protect personnel and the environment from adverse consequences of asset failures.
Reliability Analysis
Reliability analysis within criticality assessment involves delving into historical performance data, failure rates, and mean time between failures (MTBF) of assets. By scrutinizing these metrics, organizations pinpoint assets susceptible to recurrent breakdowns or downtime.
This insight enables proactive maintenance strategies to enhance reliability and uptime. Understanding the reliability of assets aids in allocating resources more effectively, optimizing maintenance schedules, and ensuring smoother operations. It’s a proactive approach that minimizes disruptions and adapts a culture of continuous improvement, driving long-term reliability and performance gains across the organization.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is a strategic evaluation in the criticality analysis that compares the cost associated with asset failure against the cost of asset maintenance activities. It involves evaluating the potential expenses linked to repairs, downtimes, and replacements against the cost of preventive maintenance measures.
The criticality assessment process enables organizations to make informed decisions about allocating maintenance budgets and investments and helps them achieve optimal Return on Investment (ROI).
By conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to understand the criticalities, businesses can prioritize maintenance activities, identify the areas for improvement, and ensure that resources are utilized efficiently to minimize cost while maximizing the performance and criticality of assets.
What is Business Criticality?
Business criticality refers to the degree of importance an asset contributes to a business or organization’s overall success and functioning. It involves assessing the impact of an asset’s failure or downtime on business operations, productivity, safety, and financial performance.
In asset maintenance, these levels categorize assets based on their importance to business operations. These levels in criticality analysis help prioritize maintenance activities and allocate resources effectively.
The business criticality levels commonly used in asset maintenance include:
1. Critical Assets: These are assets whose failure would significantly impact business operations, safety, or regulatory compliance.” Maintenance of critical assets is given high priority to minimize the risk of downtime.”
2. High-Priority Assets: These assets are essential for maintaining efficiency and productivity but may have a different criticality level than critical assets. Maintenance for high-priority assets is typically scheduled to minimize disruptions and ensure optimal performance.
3. Medium-Priority Assets: These assets contribute to business operations but are less critical than critical or high-priority assets. Maintenance for medium-priority assets is essential for preventing issues impacting efficiency and performance.
4. Low-Priority Assets: These assets have minimal impact on business operations and may not require immediate attention. Maintenance for low-priority assets is often scheduled based on cost-effectiveness and resource availability.
By categorizing assets based on their business criticality levels, organizations can prioritize maintenance efforts, allocate resources efficiently, and minimize the risk of unplanned downtime or failures that could negatively impact business operations.
Types of Maintenance Priority Supported by CMMS Platforms
Various computerized maintenance management platforms support diverse criticality levels according to their requirements. Like criticality analysis, Fogwing Asset Plus, a smart CMMS platform for asset maintenance and performance monitoring, utilizes SLA (Service Level Agreement) policies to analyze the priority of maintenance tasks according to the asset criticality levels. Organizations use these policies to conduct criticality analysis for maintenance purposes.
Fogwing Asset Plus supports four types of priority while considering asset criticality assessment: “Urgent, High, Medium, and Low.” The SLA policies guide target dates for maintenance tasks, defining response and resolution times to streamline workflow efficiency.
By categorizing maintenance tasks into these four priority levels, the Fogwing Asset Plus CMMS Platform enables organizations to prioritize resources effectively, allocate human resources efficiently, and ensure critical assets receive the attention required to operate reliably and safely. This prioritization framework, with criticality analysis, helps streamline maintenance workflows, minimize downtime, and optimize asset performance across the organization.
Fogwing Asset Plus Platform’s service level agreement feature enables maintenance managers to prioritize their asset maintenance tasks effectively. Users can define their priorities by setting an acknowledgment time for maintenance and a work order target time.
The Fogwing Asset Plus platform lets users easily track and manage maintenance work orders against the SLA policies. The users can now easily trigger email escalations to the responsible maintenance team at various crucial stages, ensuring everyone stays on track.
It helps optimize maintenance timelines and ensures higher asset reliability. The Fogwing Asset Plus platform suggests work order target dates based on the defined SLA policies. Explore the Fogwing Asset Plus platform to see how its advanced features transform your maintenance process.
Levels of Criticalities
Criticality analysis is a fundamental aspect of maintenance management, guiding organizations in prioritizing resources and actions based on the potential impact of asset failures. By categorizing assets into different criticality levels, ranging from high to low, asset criticality assessment helps determine the significance of each asset to business operations and assess the consequences of their malfunction.
Here are the levels of criticality and their role in shaping maintenance strategies and ensuring operational reliability:
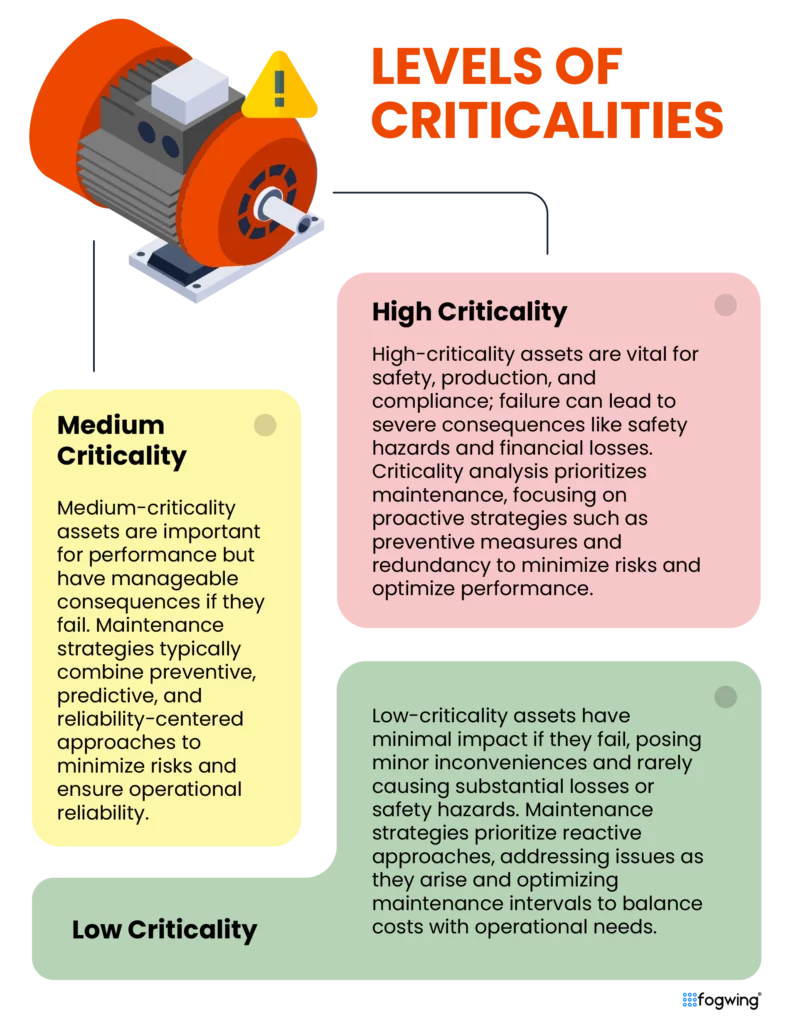
High Criticality
Organizations classify assets as high criticality when they are vital for ensuring safety, uninterrupted production processes, and regulatory compliance. The failures of assets with high criticality levels can lead to harsh consequences, including regulatory violations, safety hazards, prolonged downtime, and substantial financial losses.
Criticality analysis allows organizations to prioritize maintenance by systematically assessing the importance of each asset in their operations. Maintenance strategies for high asset criticality typically involve proactive measures like preventive maintenance, condition monitoring, and redundancy to minimize the risk of failures and ensure optimal asset performance.
Medium Criticality
In criticalities, Assets categorized as medium criticality have significant operational roles and play a major role in performance. However, they have less severe consequences if they fail than high-criticality assets. The malfunction of medium criticality level assets can lead to disruptions, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance costs.
The impact of the failures of these assets is generally less severe and manageable. Maintenance strategies for medium criticality assets may involve a combination of preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and reliability-centered maintenance to mitigate risks and maintain operational reliability.
Low Criticality
In criticality analysis, assets categorized as low criticality have a minimum impact on businesses if they fail to operate and typically do not pose significant safety risks or disrupt production processes. The failures of low criticality level assets may result in minor inconveniences or destruction, and they rarely cause substantial financial losses or safety hazards.
Maintenance strategies for low-critical assets often focus on reactive maintenance approaches, addressing issues as they arise and optimizing maintenance intervals to balance costs with operational requirements.
Applications of Criticality Analysis
Criticality analysis in maintenance is pivotal in asset maintenance management across various industries, offering several critical applications. It is a versatile tool with applications extending beyond routine maintenance. Understanding how to leverage this analysis enhances asset reliability and contributes to broader organizational objectives.
Critical applications of Criticality Analysis in various contexts within industrial & organizational settings:
1. Prioritizing Maintenance Activities: Criticality analysis for maintenance purposes helps organizations identify assets with the highest impact on operations, allowing them to prioritize maintenance activities accordingly. Critical assets undergo more frequent and proactive maintenance activities to minimize asset downtime or failure risk.
2. Resource Allocation: By categorizing assets based on their levels of criticality, organizations can more effectively allocate resources such as time, human resources, and budget. Higher criticality assets receive greater attention and resources than medium and low criticality assets to ensure reliability and availability.
3. Criticality Analysis in Risk Mitigation: Understanding the criticality of assets enables organizations to assess potential risks associated with asset downtime or failures. With criticality assessment, organizations can concentrate on high-criticality assets, as it helps them identify and mitigate the risk associated with equipment failure. Maintenance efforts can reduce risks related to safety hazards, production disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, and financial losses.
4. Optimal Strategic Planning: Criticality analysis for maintenance purposes plays a pivotal role in long-term asset planning by aligning asset management with business goals. It aims to prioritize investment, directing resources toward critical assets essential for effectively achieving business objectives. Understanding asset criticality can help organizations develop strategic plans that optimize equipment performances, minimize risks, and support long-term sustainability.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making: Criticality analysis provides valuable objective insights based on data, reducing the organization’s reliance on subjective judgments. It helps businesses and stakeholders make asset management, investment prioritization, and resource planning decisions by considering the potential impact of asset failures on overall business objectives. The data-driven approach of criticality analysis for maintenance purposes helps organizations continuously improve asset management practices.
How to Perform Criticality Analysis?
Asset criticality assessment is a process that involves evaluating and categorizing an organization’s assets based on their importance to the overall operations of an organization. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform Criticality Analysis.
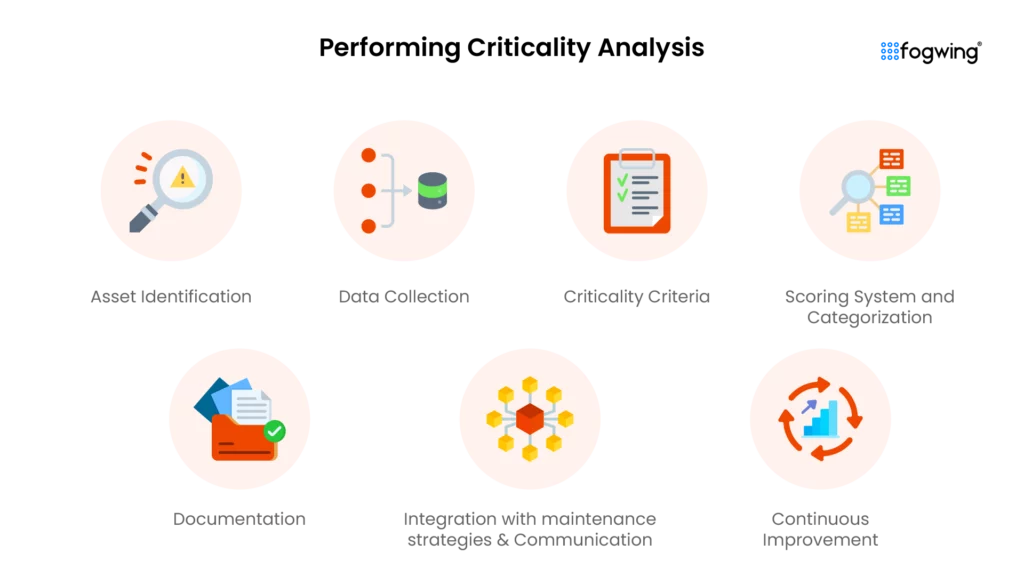
1. Asset Identification: The first step in criticality assessment begins with asset identification. Create an inventory of all assets within the system and clearly define each asset along with its specific functionality and name within the operational landscape.
2. Data Collection: Once you have completed asset identification, the next step is to collect adequate data related to those assets, including historical performance, failure rates, and maintenance records. Consider input from various stakeholders, including operations and maintenance teams, to gain a holistic perspective.
3. Criticality Criteria: Establishing clear criteria for assessing the criticality of assets is an essential step in performing criticality analysis. You may consider safety implications, environmental impact, production downtime, and financial consequences. Customize and tailor the criteria to align with the organization’s goals and priorities.
4. Scoring System and Categorization: Develop an application criticality matrix to evaluate assets objectively, considering factors like reliability and the consequence of failure. Assign scores to each factor, reflecting their weighted importance in determining asset criticalities.
Use the scored data to categorize assets into criticality levels, like high, medium, and low. And set clear thresholds for each criticality level to streamline the categorization process and guide decision-making effectively.
5. Documentation: Once you finish scoring and categorizing, document the analysis results, including the criticality level assigned to each asset. Provide a rationale for the assigned criticality levels, detailing the factors influencing the categorization.
6. Review and Iteration: Schedule regular reviews of criticality analysis to ensure its relevance and accuracy. Incorporate feedback from maintenance activities and other operational insights into the analysis. Be adaptive to changes in the system, technology, or business goals that may impact criticality levels.
7. Integration with maintenance strategies & Communication: To efficiently maintain critical assets, aligning your maintenance strategies with your asset criticality assessment results is essential. You can optimize resource allocation by dedicating a proportional number of resources based on the criticality level.
It is crucial to communicate with relevant stakeholders to promote transparency and informed decision-making. Building trust and collaboration among teams is essential to ensure transparency in decision-making processes regarding asset criticality levels.
8. Continuous Improvement: Criticality analysis is not a one-time task but a dynamic process contributing to ongoing asset maintenance and management improvements. Learn from the results and use insights from the analysis to improve asset management practices continuously. Adjust strategies based on the outcomes of criticality assessment to enhance overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, criticality analysis is a cornerstone in effective asset maintenance strategies, enabling organizations to prioritize resources and actions based on the potential impact of asset failures. By systematically assessing asset criticality, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, minimize downtime, and optimize asset performance and reliability.
By understanding asset prioritization, risk assessment, reliability analysis, and cost-benefit analysis, businesses can develop proactive maintenance strategies that enhance operational safety, mitigate risks, and maximize investment returns. Leveraging criticality analysis fosters data-driven decision-making, optimal resource allocation, and continuous improvement, ensuring long-term sustainability and operational excellence across various industries.


